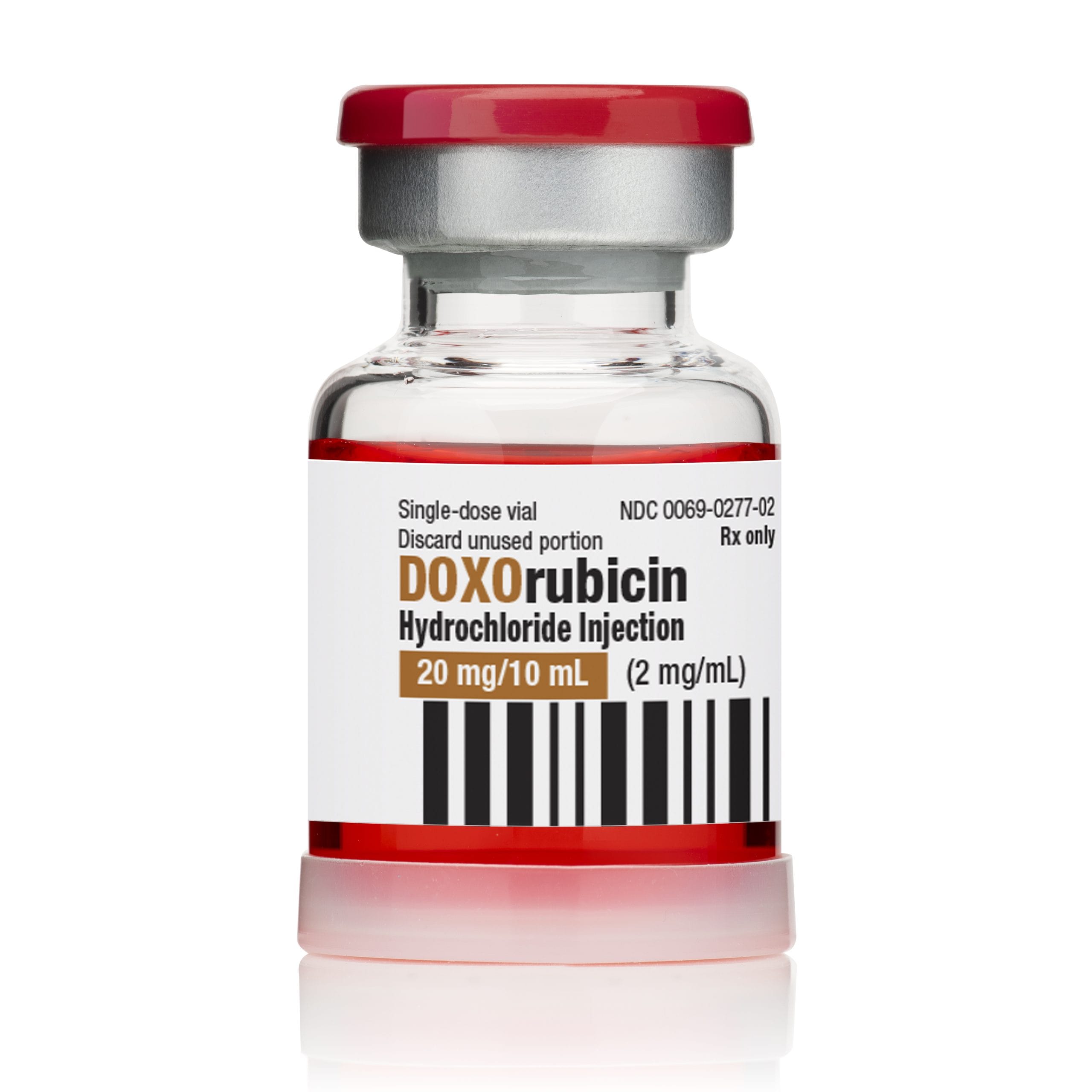
Doxorubicin is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a wide range of cancers. It belongs to a group of drugs called anthracyclines and works by interfering with the growth and division of cancer cells. It is commonly used as part of combination chemotherapy protocols in both human and veterinary medicine.
Benefits
- Effective against various types of cancer, including lymphomas, sarcomas, and carcinomas
- Works by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, preventing them from multiplying
- Often included in multi-drug treatment plans to improve overall effectiveness
- May help reduce tumor size and slow disease progression
Dosage
- Dosage depends on factors such as body surface area, overall health, and type of cancer
- Usually administered intravenously by a healthcare professional
- Frequency of administration varies (commonly every 2 to 3 weeks)
- Requires close monitoring during treatment
Warnings and Precautions
- Can cause damage to the heart (cardiotoxicity); cardiac monitoring may be required
- Suppresses bone marrow activity; regular blood tests are necessary
- May cause severe gastrointestinal side effects
- Not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding
- Use with caution in individuals with liver disease or existing infections
How to Use
- Administered in a clinical setting under professional supervision
- Hydration and supportive care may be needed before and after treatment
- Patients should follow all safety instructions provided by their healthcare provider
- Report any side effects or symptoms promptly
Storage
- Stored under controlled conditions by healthcare providers
- Keep away from heat, light, and moisture
- Not for home storage or handling without professional direction
Side Effects
- Common: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, hair loss, fatigue, low blood cell counts
- Serious: Heart problems, severe infections, mouth sores, allergic reactions
- Seek medical attention if symptoms like shortness of breath, chest pain, or high fever occur